1 Introduction
You certainly know how that Varnish is a very good caching solution but the major problem is you can't use it for SSL connections. Fortunately there is a solution called "Offload SSL" which decrypt the SSL, send it to the cache system and return crypted flow. This schema will help you more on understanding the purpose of it :
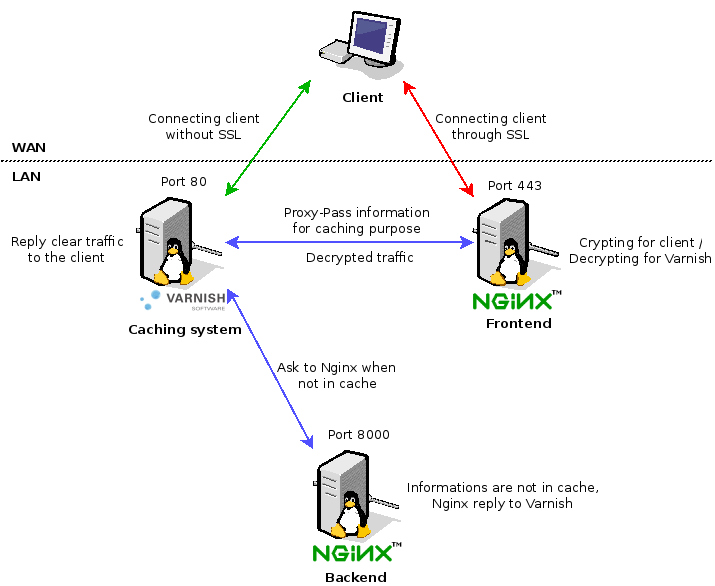
How the thing goes ?
- Let's start with the simplest thing : the non SSL traffic :
- The client requests data to the Varnish server :
- If Varnish gots information -> it replies directly to the client
- If Varnish doesn't got information :
- It forwards connections to the Nginx in backend which reply to Varnish for caching
- Send back results to the client
- For the SSL traffic now :
- The client request data to the Nginx Frontend with SSL
- Nginx decrypt SSL traffic and forward the clear traffic to Varnish
- Varnish check it's cache and decide to forward to the Nginx backend if data is not in cache
- Nginx backend reply the required data to Varnish
- The data in Varnish are sent back to the Nginx Frontend for SSL reencapsulation
- Nginx Front end send the result to the client
Of course you don't need to have multiple machine to make it work. Here I'm using a single machine and a single Nginx instance listening on 2 different ports.
2 Installation
You need to have of course Nginx PHP-FPM and Varnish installed :
 aptitude aptitude
|
aptitude install varnish nginx php5-fpm openssl |
Then create SSL certificates or install yours :

|
mkdir -p /etc/nginx/ssl
cd /etc/nginx/ssl
openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -out server.crt -keyout server.key |
3 Configuration
3.1 Nginx
Regarding the Nginx configuration, here is the configuration for the Frontend (SSL) and the backend (8000) on the same Nginx instance :
 /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
|
# SSL VirtualHost
server {
# SSL Listen port
listen 443 ssl;
# Certificates
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/server.key;
# Resumption
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
# Timeout
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# Security options
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-RC4-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-RC4-SHA:ECDH-ECDSA-RC4-SHA:ECDH-RSA-RC4-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:RC4-SHA;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
server_name vhost.deimos.fr;
# Proxy Pass to Varnish # Add headers to recognize SSL location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:80; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port 443; proxy_set_header X-Secure on; }}
# Clear VirtualHost
server { listen 8000;
server_name vhost.deimos.fr;
root /usr/share/nginx/www/test;
index index.php;
set_real_ip_from 127.0.0.1; real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For; real_ip_recursive on;
access_log /var/log/nginx/vhost.deimos.fr_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/vhost.deimos.fr_error.log;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
}
} |
3.2 Varnish
First of all, change the configuration to have a cache RAM and listen on 80 port :
 /etc/default/varnish /etc/default/varnish
|
...
# Should we start varnishd at boot? Set to "yes" to enable.
START=yes
[...]
DAEMON_OPTS="-a :80 \ -b localhost:8000 \ -S /etc/varnish/secret \
-p thread_pools=2 \
-p thread_pool_min=100 \
-p thread_pool_max=2000 \
-p thread_pool_add_delay=2 \
-p session_linger=50 \
-s malloc,512m"
[...] |
Then configure the forward to the Nginx backend and elements to cache :
 /etc/varnish/default.vcl /etc/varnish/default.vcl
|
# This is a basic VCL configuration file for varnish. See the vcl(7)
# man page for details on VCL syntax and semantics.
#
# Default backend definition. Set this to point to your content
# server.
#
# Redirect to Nginx Backend if not in cachebackend default { .host = "127.0.0.1"; .port = "8000";}
acl purge {
"127.0.0.1";
}
# vcl_recv is called whenever a request is received
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.restarts == 0) { if (req.http.x-forwarded-for) { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = req.http.X-Forwarded-For + ", " + client.ip; } else { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip; } } if (req.http.X-Real-IP) { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = req.http.X-Real-IP; } else { set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip; }
# Serve objects up to 2 minutes past their expiry if the backend
# is slow to respond.
set req.grace = 120s;
set req.backend = default;
if (!req.http.X-Forwarded-Proto) { set req.http.X-Forwarded-Proto = "http"; set req.http.X-Forwarded-Port = "80"; set req.http.X-Forwarded-Host = req.http.host; }
# This uses the ACL action called "purge". Basically if a request to
# PURGE the cache comes from anywhere other than localhost, ignore it.
if (req.request == "PURGE")
{if (!client.ip ~ purge)
{error 405 "Not allowed.";}
return(lookup);}
# Pass any requests that Varnish does not understand straight to the backend.
if (req.request != "GET" && req.request != "HEAD" &&
req.request != "PUT" && req.request != "POST" &&
req.request != "TRACE" && req.request != "OPTIONS" &&
req.request != "DELETE")
{return(pipe);} /* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */
# Pass anything other than GET and HEAD directly.
if (req.request != "GET" && req.request != "HEAD")
{return(pass);} /* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */
# Pass requests from logged-in users directly.
if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie)
{return(pass);} /* Not cacheable by default */
# Pass any requests with the "If-None-Match" header directly.
if (req.http.If-None-Match)
{return(pass);}
# Force lookup if the request is a no-cache request from the client.
if (req.http.Cache-Control ~ "no-cache")
{ban_url(req.url);}
return(lookup);
}
sub vcl_pipe {
# This is otherwise not necessary if you do not do any request rewriting.
set req.http.connection = "close";
}
# Called if the cache has a copy of the page.
sub vcl_hit {
if (req.request == "PURGE")
{ban_url(req.url);
error 200 "Purged";}
if (!obj.ttl > 0s)
{return(pass);}
}
# Called if the cache does not have a copy of the page.
sub vcl_miss {
if (req.request == "PURGE")
{error 200 "Not in cache";}
}
# Called after a document has been successfully retrieved from the backend.
sub vcl_fetch {
set beresp.grace = 120s;
if (beresp.ttl < 48h) {
set beresp.ttl = 48h;}
if (!beresp.ttl > 0s)
{return(hit_for_pass);}
if (beresp.http.Set-Cookie)
{return(hit_for_pass);}
if (req.http.Authorization && !beresp.http.Cache-Control ~ "public")
{return(hit_for_pass);}
}
sub vcl_pass {
return (pass);
}
sub vcl_hash {
hash_data(req.url);
if (req.http.host) {
hash_data(req.http.host);
} else {
hash_data(server.ip);
}
return (hash);
}
sub vcl_deliver {
# Debug remove resp.http.Via; remove resp.http.X-Varnish; # Add a header to indicate a cache HIT/MISS if (obj.hits > 0) { set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT"; set resp.http.X-Cache-Hits = obj.hits; set resp.http.X-Age = resp.http.Age; remove resp.http.Age; } else { set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS"; } return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_error {
set obj.http.Content-Type = "text/html; charset=utf-8";
set obj.http.Retry-After = "5";
synthetic {"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>"} + obj.status + " " + obj.response + {"</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Error "} + obj.status + " " + obj.response + {"</h1>
<p>"} + obj.response + {"</p>
<h3>Guru Meditation:</h3>
<p>XID: "} + req.xid + {"</p>
<hr>
<p>Varnish cache server</p>
</body>
</html>
"};
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_init {
return (ok);
}
sub vcl_fini {
return (ok);
} |
4 Testing
The testing part is should be applied in the good order. For my personal usages, I waste too much time because I didn't made the proper checks before. The things to check should be in that order :
- Check Nginx backend on port 8000
- Check Varnish access on port 80
- Check SSL Nginx frontend on port 443
Add this index in your vhost server to get your header informations directly on the page :
 /usr/share/nginx/www/test/index.php /usr/share/nginx/www/test/index.php
|
<?php
echo "Show all headers :\n";
foreach($_SERVER as $h=>$v)
if(ereg('HTTP_(.+)',$h,$hp))
echo "<li>$h = $v</li>\n";
header('Content-type: text/html');
?> |
To test it you can use curl :
 curl curl
|
> curl -I http://url
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Last-Modified: Tue, 07 Jan 2014 10:40:39 GMT
Expires: Tue, 07 Jan 2014 11:40:39 GMT
Pragma: public
Cache-Control: public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate
Etag: db7025811efc180e605972eb57550b68
X-Powered-By: W3 Total Cache/0.9.3
Vary: Accept-Encoding
X-Pingback: http://blog.deimos.fr/xmlrpc.php
Date: Tue, 07 Jan 2014 10:56:23 GMT
X-Varnish: 964417199 964417198
Age: 4
Via: 1.1 varnish
Connection: keep-alive |
Use wget :
 wget wget
|
> wget -SS http://url
HTTP request sent, awaiting response...
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Last-Modified: Tue, 07 Jan 2014 10:40:39 GMT
Expires: Tue, 07 Jan 2014 11:40:39 GMT
Pragma: public
Cache-Control: public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate
Etag: db7025811efc180e605972eb57550b68
X-Powered-By: W3 Total Cache/0.9.3
Vary: Accept-Encoding
X-Pingback: http://url
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Date: Tue, 07 Jan 2014 10:57:22 GMT
X-Varnish: 964417220 964417198
Age: 63
Via: 1.1 varnish
Connection: keep-alive
Length: unspecified [text/html] |
Or you can also use LiveHTTPHeader Firefox extension to see headers. Now press keyboard :
- Ctrl+r : to reload the page (the second try should be cached)
- Ctrl+Shift+r : to reload the page asking the server to not deliver cached informations
If you try to access in https, you should get something like that :
Show all headers :
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_HOST = test.deimos.fr
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PROTO = https
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PORT = 443
HTTP_HOST = 127.0.0.1
HTTP_USER_AGENT = Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:26.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/26.0
HTTP_ACCEPT = text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
HTTP_ACCEPT_LANGUAGE = fr,fr-fr;q=0.8,en-us;q=0.5,en;q=0.3
HTTP_ACCEPT_ENCODING = gzip, deflate
HTTP_COOKIE = _pk_id.1.5a2c=dfe5af08663a76b5.1388449087.3.1389005232.1388454622.; __qca=P0-1050834221-1388449087452; __cfduid=daa3baabbe79eb123b50f511c058dd29c1389819921950
HTTP_CACHE_CONTROL = max-age=0
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR = 222.2.20.132, 127.0.0.1
HTTP_X_VARNISH = 1929521662
5 References
http://mikkel.hoegh.org/blog/2012/07/24/varnish-as-reverse-proxy-with-nginx-as-web-server-and-ssl-terminator/
