MariaDB Operator: Run full featured MariaDB in Kubernetes
Introduction
MariaDB is a community-developed, commercially supported fork of the MySQL relational database management system. MariaDB is a drop-in replacement for MySQL and is designed to be a more robust, scalable, and secure database solution.
The MariaDB Operator is a tool that allows you to run a full featured MariaDB in Kubernetes. It is a great way to run a MariaDB server in Kubernetes and it is a great way to manage your MariaDB server in Kubernetes.
The benefits are:
- It is a full featured MariaDB server solution
- It is a great way to run a MariaDB server in Kubernetes
- You don't have to manage the MariaDB server manually for backups, upgrades, etc.
- There are build-in ways to scale the MariaDB server
- Easily extensible with MaxScale, Replications with auto-failover, GaleraDB...and easily customizable
Before starting, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster.
Installation
First, you need to install the MariaDB Operator with Helm:
For best practices and later usage, I advise to set the metrics and resources like:
You can update the mariadb-operator chart with the following values file (simply add -f mariadb-operator-override-values.yaml to the helm install command).
If you check your pods, you should see something like this:
Single instance configuration
You can configure a single instance of MariaDB with the following configuration:
Regarding the StorageClass, I'm using OpenEBS LVM for the best performance. It's not mandatory and you can use any other storage class. However, for maximum performances, you should use local storage.
Apply this configuration with kubectl:
And you should see the MariaDB instance running:
Create a user
You can decide to create a dedicated secret for this new user or use the same secret as the MariaDB instance. Here we're going to update the existing secret:
You can now create a user on the MariaDB instance with the following configuration:
You can now apply this configuration with kubectl:
Grant privileges
You can grant privileges to a user with the following configuration:
High availability
The MariaDB Operator also supports multiple High Availability solutions like:
- Replications with auto-failover: a master-master replication solution with auto-failover capabilities, also called SemiSync replication.
- Galera: a multi-master replication solution with auto-failover capabilities.
- MaxScale: a proxy solution with failover and load balancing capabilities
We'll take a look here at the Replications with auto-failover solution. I like this one because it's built-in and it's very easy to configure for a home lab. Prefer the Galera solution if you need a multi-master solution. And use MaxScale if you need a more complex solution with failover and load balancing capabilities.
Replications with auto-failover
Here is a configuration with only 2 nodes (not perfect because of the missing Qorum) but it's a good start for a home lab.
Once applied, you can check replication status with:
MaxScale
MaxScale is a proxy solution with failover and load balancing capabilities. It's a great way to scale your MariaDB instance. It's also a great way to have a more complex solution with failover and load balancing capabilities.
Here is a configuration with 2 nodes (not perfect because of the missing Qorum) but it's a good start for a home lab. It's pretty similar to the replication configuration but with a MaxScale proxy in front of the MariaDB instances, a few configuration changes are needed:
And now the MaxScale configuration:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 | |
Deploy the MariaDB and MaxScale configuration with:
You can check the MaxScale configuration with the following command:
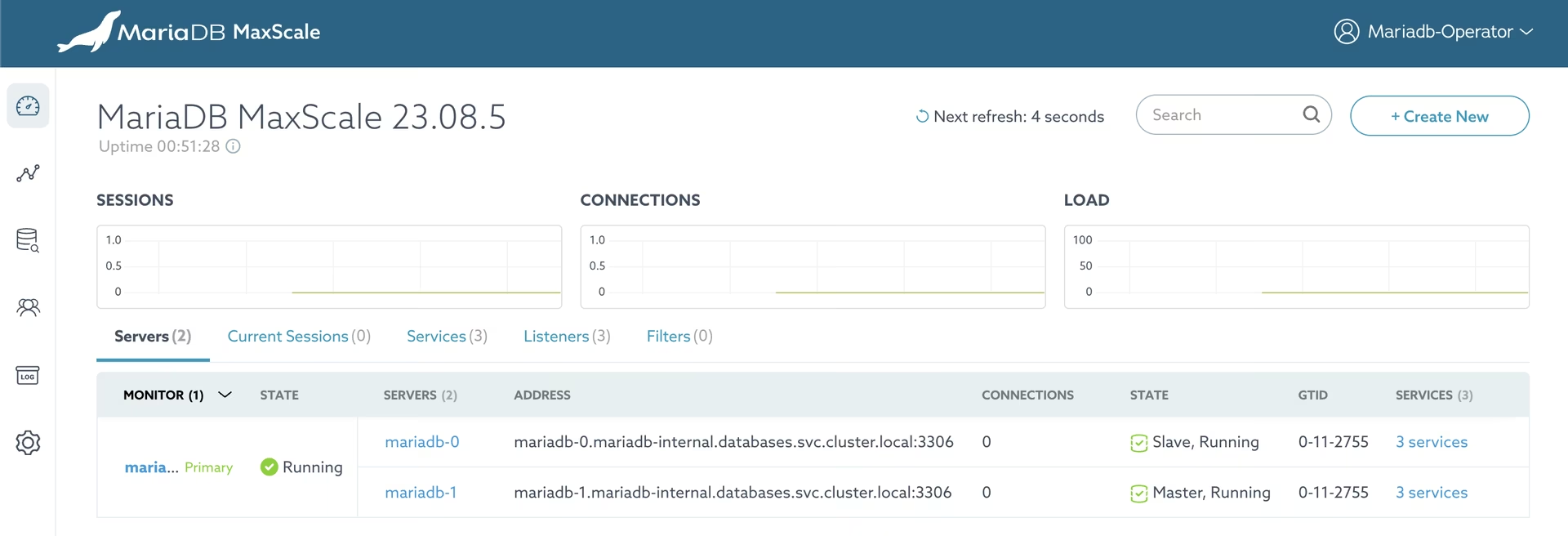
MaxScale admin GUI access
You can access the MaxScale admin GUI with the Metallb address (here: http://192.168.0.2:8989) or you can create a port-forwarding to access it from your local machine:
Then access to http://localhost:8989/ to access the MaxScale admin GUI.
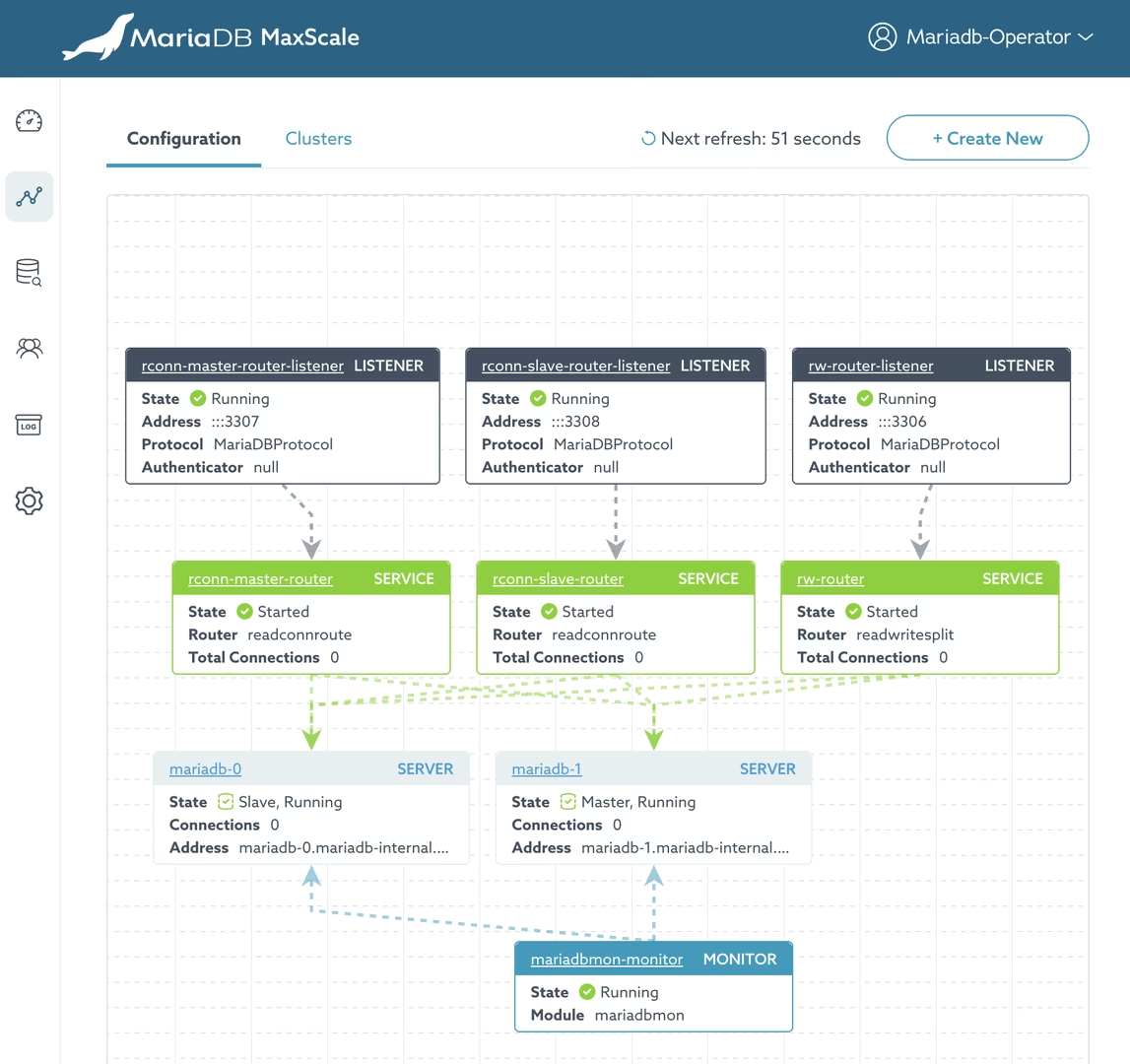
You can find the credentials inside the secret maxscale-repl-admin and use the mariadb-operator username as login. Then you'll be able to see the MaxScale configuration and the status of the replication:
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues, you can check the logs of the MariaDB instance with the following command: