OpenBoot PROM, BIOS Management
Introduction
The PROM is the equivalent of the BIOS or EFI on a standard x86 system.
Approach
To know your PROM version:
/usr/platform/`uname -m`/sbin/prtdiag -v
or
prtconf -V
NVRAM
The NVRAM can be modified by a user to change some options on the machine:
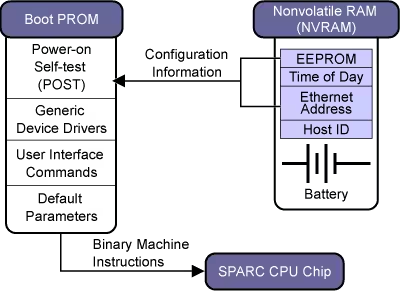
Once the NVRAM is stored on the chipset, during the PROM call at boot, it will check the user’s preferences at the NVRAM level in order to apply them.
Diagnostic
To enter Diagnostic mode, press: Stop+D
To stop an ongoing diagnostic: Stop+A
Disabling Keyboard Use
If you want to disable the keyboard at boot, edit the file /etc/default/kbd and uncomment this line:
KEYBOARD_ABORT=disable
Save, exit and run this command:
kbd -i
After doing this, you’ll only have access to the Stop+A key sequence.
PROM Commands
I intentionally left the descriptions in English to avoid translation errors:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| banner | Displays the power-on banner |
| boot | Boots the system |
| help | Lists the main help categories |
| printenv | Displays all parameters’ current and default values |
| setenv | Sets the specified NVRAM parameter to some value |
| reset-all | Resets the entire system; similar to a power cycle |
| set-defaults | Resets all parameter values to the factory defaults |
| sifting text | Displays the FORTH commands containing text |
| .registers | Displays the contents of the registers |
| probe-scsi | Identifies the devices on the internal Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) bus |
| probe-scsi-all | Identifies the devices on all SCSI buses |
| probe-ide | Identifies devices on the internal integrated device electronics (IDE) bus |
| probe-fcal-all | Identifies devices on all Fibre Channel loops |
| show-devs | Displays the entire device tree |
| devalias | Identifies the current boot device alias for the system |
| nvalias | Creates a new device alias name |
| nvunalias | Removes a device alias name |
| show-disks | Displays and allows a selection of device paths for the disks to be used for nvalias |
| sync | Manually attempts to flush memory and synchronize file systems |
| test | Runs self-tests on specified devices |
Banner
ok banner
Sun Ultra 5/10 UPA/PCI (UltraSPARC-IIi 360MHz), Keyboard Present
OpenBoot 3.31, 128 MB (50 ns) memory installed, Serial #11888271.
Ethernet address 8:0:20:b5:66:8f, Host ID: 80b5668f.
Boot
- This provides an interactive mode:
ok boot -a
Enter filename [kernel/sparcv9/unix]:
Enter default directory for modules [/platform/SUNW,UltraAX-i2/kernel
/platform/sun4u/kernel /kernel /usr/kernel]:
Name of system file [etc/system]:
SunOS Release 5.10 Version s10 64-bit
Copyright 1983-2004 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Use is subject to license terms.
root filesystem type [ufs]:
Enter physical name of root device
[/pci@1f,0/pci@1/scsi@8/disk@0,0:a]:
- To boot from a CD/DVD:
ok boot cdrom -s
- Reconfigure the boot:
ok boot -r
- Enable verbose mode:
ok boot -v
Help
Here’s the help command:
ok help
Enter 'help command-name' or 'help category-name' for more help
(Use ONLY the first word of a category description)
Examples: help system -or- help nvramrc
Categories:
boot (Load and execute a program)
nvramrc (Store user defined commands)
system configuration variables (NVRAM variables)
command line editing
editor (nvramrc editor)
resume execution
devaliases (Device aliases)
diag (Diagnostics commands)
ioredirect (I/O redirection commands)
misc (Miscellaneous commands)
ok
Here are some examples:
ok help boot
ok help nvramrc
ok help diag
ok help misc
printenv
This command lists all NVRAM preferences:
ok printenv
Variable Name Value Default Value
tpe-link-test? true true
scsi-initiator-id 7 7
keyboard-click? false false
keymap
ttyb-rts-dtr-off false false
ttyb-ignore-cd true true
ttya-rts-dtr-off false false
ttya-ignore-cd true true
ttyb-mode 9600,8,n,1,- 9600,8,n,1,-
ttya-mode 9600,8,n,1,- 9600,8,n,1,-
pcia-probe-list 1,2,3,4 1,2,3,4
pcib-probe-list 1,2,3 1,2,3
mfg-mode off off
diag-level max max
#power-cycles 273
output-device screen screen
input-device keyboard keyboard
boot-command boot boot
auto-boot? true true
diag-device net net
boot-device disk net disk net
local-mac-address? false false
screen-#columns 80 80
screen-#rows 34 34
use-nvramrc? false false
nvramrc devalias pgx24 /pci1f,0 ...
security-mode none
security-password
security-#badlogins 0
diag-switch? false false
ok
To display only one parameter:
ok printenv boot-device
boot-device = disk net
Setenv
If the autoboot parameter is set to true, the system will boot automatically, otherwise you’ll get a prompt:
ok printenv auto-boot?
auto-boot? = true
ok
ok setenv auto-boot? false
auto-boot? = false
To turn off the machine, empty the buffers and registers, use this command:
ok reset-all
Resetting ...
Set-defaults
To reset all parameters to default values, use this command:
ok set-defaults
Setting NVRAM parameters to default values.
ok
To reset only one parameter (here diag-level):
ok set-default diag-level
Probe
To find all available probe commands:
ok sifting probe
(f006c954) probe-all (f006c5a0) probe-all (f006c378) probe-ide
(f006c1e8) probe-pci-slot (f006bc8c) probe-scsi
(f006bd78) probe-scsi-all (f0060fe8) probe-pci
(output truncated)
This command may hang the system if a Stop-A or halt command has been executed. Please type reset-all to reset the system before executing this command.
Do you wish to continue? (y/n) n
If portions of Solaris OS were in RAM when the system was suspended, the probe command could shut down the machine. To avoid this:
ok setenv auto-boot? false
ok reset-all
Otherwise you can use .registers:
ok .registers
Normal Alternate MMU Vector
0: 0 0 0 0
1: 0 0 0 0
2: 0 0 0 0
3: 0 0 0 0
4: 0 0 0 0
(output edited for brevity)
%PC 0 %nPC 0
%TBA 0 %CCR 0 XCC:nzvc ICC:nzvc
Check that all values are at 0, otherwise the system may shut down.
Probe-scsi
For a SCSI device, use this command:
ok probe-scsi
Target 1
Unit 0 Disk FUJITSU MAB3045S SUN4.2G17059825M62990
Target 3
Unit 0 Disk IBM DDRS34560SUN4.2GS98E99255C5917
(C) Copyright IBM Corp.
1997. All rights reserved.
Target 6
Unit 0 Removable Read Only device SONY CDROM
Probe-scsi-all
Same but for all SCSI devices:
ok probe-scsi-all
/pci@1f,0/pci@1/pci@1/SUNW,isptwo@4
Target 3
Unit 0 Disk FUJITSU MAB3045S SUN4.2G1907
Target 4
Unit 0 Removable Tape EXABYTE EXB-8505SMBANSH20090
Probe-ide
For IDE devices:
ok probe-ide
Device 0 ( Primary Master )
ATA Model : ST 38420A (DISK)
Device 1 ( Primary Slave )
Not Present
Device 2 ( Secondary Master )
Removable ATAPI Model : CRD-8322B (CD-ROM)
Device 3 ( Secondary Slave )
Not Present
Show-dev
To list all devices:
ok show-devs
/SUNW,UltraSPARC-IIi@0,0
/pci@1f,0
/virtual-memory
/memory@0,10000000
/pci@1f,0/pci@1
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/SUNW,m64B@2
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/network@1,1
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/cdrom
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/SUNW,CS4231@14,200000
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/flashprom@10,0
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/eeprom@14,0
/pci@1f,0/pci@1/pci@1
/pci@1f,0/pci@1/pci@1/SUNW,isptwo@4
(output truncated)
ok
Devalias
To identify boot devices:
ok devalias
screen /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/SUNW,m64B@2
net /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/network@1,1
cdrom /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/cdrom@2,0:f
disk /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk@0,0
disk3 /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk@3,0
disk2 /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk@2,0
disk1 /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk@1,0
disk0 /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk@0,0
ide /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3
floppy /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/fdthree
ttyb /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/se:b
ttya /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/se:a
keyboard! /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/su@14,3083f8:forcemode
keyboard /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/su@14,3083f8
mouse /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/su@14,3062f8
name aliases
To boot with the devices above:
ok boot
nvalias
To create an alias for an existing device:
nvalias aliasname device_path
To put this alias in NVRAM:
devalias aliasname device_path
Here’s an example:
ok show-disks
a) /pci@1f,0/pci@1/scsi@1,1/disk
b) /pci@1f,0/pci@1/scsi@1/disk
c) /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/cdrom
d) /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk
e) /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ebus@1/fdthree@14,3023f0
q) NO SELECTION
Enter Selection, q to quit: d
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk has been selected.
Type ^Y (Control-Y) to insert it in the command line.
e.g. ok nvalias mydev ^Y
for creating devalias mydev for
/pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk
ok nvalias mydisk ^y
To copy the selected path, press Ctrl+Y, then add the LUN (Logical Unit Number) of the disk:
ok nvalias mydisk /pci@1f,0/pci@1,1/ide@3/disk@0,0:a
To add the boot to this new alias:
ok setenv boot-device mydisk
boot-device = mydisk
ok boot
nvualias
To remove an alias:
ok nvunalias aliasname
Example:
ok nvunalias mydisk
ok setenv boot-device disk
boot-device = disk
ok reset-all
Resetting ...
Then use this command to see the parameters:
/usr/sbin/eeprom
eeprom
To list all parameters with their values:
eeprom
To list only one value:
eeprom boot-device
boot-device=disk
To change the value of a command:
eeprom boot-device=disk2
eeprom auto-boot?=true
Synchronize the PROM
To synchronize the PROM if the system is not responding, for example:
ok sync
Last updated 29 Nov 2006, 09:51 +0200.