Load Balancing Multiple WAN Connections
Introduction
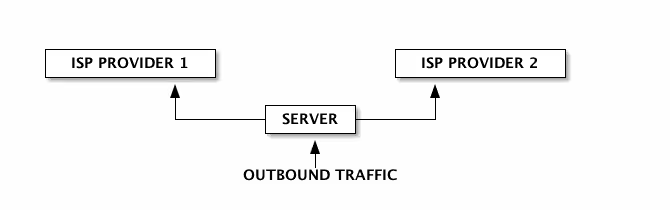
If one ISP Provider bandwidth is not enough for your needs, you can have multiple lines and load balance between them on Linux. This documentation has been done on Debian and works like a charm :-).
It contains 3 network interfaces:
- Is plugged in a special DMZ VLAN (eth0)
- The second is plugged on a dedicated VLANS to ISP1 Provider (eth1)
- The third is plugged on a dedicated VLANS to ISP2 Provider (eth2)
Internet traffic is load balanced between the two Internet accesses. In the current configuration the weight assigned to ISP1 is 3 and ISP2 1 (it means that 3 times more traffic passes through ISP1 than ISP2).
Network configuration
To do this, we are using the following configuration:
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
allow-hotplug eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 172.16.0.51
netmask 255.255.255.240
broadcast 172.16.0.63
post-up route add -net 192.168.0.0/16 gw 172.16.0.49
post-up route add -net 172.16.0.0/16 gw 172.16.0.49
post-up route add -net 10.0.0.0/8 gw 172.16.0.49
# ISP1
allow-hotplug eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 192.168.1.2
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1
# ISP2
allow-hotplug eth2
iface eth2 inet static
address 192.168.2.2
netmask 255.255.255.0
Load Balancing configuration
Create the enable_balanced_routing script (/etc/network/if-up.d/enable_balanced_routing):
#!/bin/bash
# Enable load balancing between ISP1 & ISP2
# Enable routing on eth2 up
test "${IFACE}" = 'eth2' || exit 0
function die()
{
echo "$@" >&2
exit 1
}
which ip >/dev/null 2>&1 || die "Command not found, please install it"
which ipcalc >/dev/null 2>&1 || die "Command not found, please install it"
LAN_IFACE='eth0'
LAN_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${LAN_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
LAN_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${LAN_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET1_IFACE='eth1'
INET1_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${INET1_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
INET1_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${INET1_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET1_GW='192.168.1.1'
INET1_WEIGHT=1
INET2_IFACE=${IFACE}
INET2_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${INET2_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
INET2_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${INET2_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET2_GW='192.168.2.1'
INET2_WEIGHT=3
# Create routes throught ours network in each tables
ip route add ${LAN_NET_IP} dev ${LAN_IFACE} table 100
ip route add ${INET1_NET_IP} dev ${INET1_IFACE} src ${INET1_IFACE_IP} table 100
ip route add ${INET2_NET_IP} dev ${INET2_IFACE} table 100
ip route add 127.0.0.0/8 dev lo table 100
ip route add ${LAN_NET_IP} dev ${LAN_IFACE} table 200
ip route add ${INET1_NET_IP} dev ${INET1_IFACE} table 200
ip route add ${INET2_NET_IP} dev ${INET2_IFACE} src ${INET2_IFACE_IP} table 200
ip route add 127.0.0.0/8 dev lo table 200
# Create a default route per table
ip route add default via ${INET1_GW} table 100
ip route add default via ${INET2_GW} table 200
# Assigning appropriate traffic from an interface to the corresponding table
ip rule add from ${INET1_IFACE_IP} table 100
ip rule add from ${INET2_IFACE_IP} table 200
# Force some specific routes if needed
# ip route add to x.x.x.x via ${INET1_GW} dev ${INET1_IFACE}
# ip route add to x.x.x.x via ${INET1_GW} dev ${INET1_IFACE}
# Replacing default route
ip route del default
ip route add default scope global nexthop via ${INET1_GW} dev ${INET1_IFACE} weight ${INET1_WEIGHT} nexthop via ${INET2_GW} dev ${INET2_IFACE} weight ${INET2_WEIGHT}
ip route flush cached
# If you're using ntop, you should restart it for new changes to take effect
# /etc/init.d/ntop restart &
Now let’s create the disable script (/etc/network/if-down.d/disable_balanced_routing):
#!/bin/bash
# Disable load balancing between ISP1 & ISP2
# Enable routing on eth2 down
test "${IFACE}" = 'eth2' || exit 0
which ip >/dev/null 2>&1 || die "Command not found, please install it"
which ipcalc >/dev/null 2>&1 || die "Command not found, please install it"
LAN_IFACE='eth0'
LAN_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${LAN_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
LAN_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${LAN_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET1_IFACE='eth1'
INET1_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${INET1_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
INET1_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${INET1_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET1_GW='192.168.1.1'
INET2_IFACE=${IFACE}
INET2_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${INET2_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
INET2_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${INET2_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET2_GW='192.168.2.1'
ip route del default
ip route add default via ${INET1_GW}
ip route flush cached
# Delete our network routes in each tables
ip route del ${LAN_NET_IP} dev ${LAN_IFACE} table 100
ip route del ${INET1_NET_IP} dev ${INET1_IFACE} src ${INET1_IFACE_IP} table 100
ip route del ${INET2_NET_IP} dev ${INET2_IFACE} table 100
ip route del 127.0.0.0/8 dev lo table 100
ip route del ${LAN_NET_IP} dev ${LAN_IFACE} table 200
ip route del ${INET1_NET_IP} dev ${INET1_IFACE} table 200
ip route del ${INET2_NET_IP} dev ${INET2_IFACE} src ${INET2_IFACE_IP} table 200
ip route del 127.0.0.0/8 dev lo table 200
# Delete default routes in tables
ip route del default via ${INET1_GW} table 100
ip route del default via ${INET2_GW} table 200
# Disable route traffic weight rules
ip rule del from ${INET1_IFACE_IP} table 100
ip rule del from ${INET2_IFACE_IP} table 200
# Delete specific routes
# ip route del to x.x.x.x via ${INET1_GW} dev ${INET1_IFACE}
# ip route del to x.x.x.x via ${INET1_GW} dev ${INET1_IFACE}
Add execute rights:
chmod ug+rx /etc/network/if-up.d/enable_balanced_routing /etc/network/if-down.d/disable_balanced_routing
Automatic failover
Since the ISP2 Internet access is unstable, we are using a self-made script to check it, and disable traffic through this interface if needed. This script runs in the background, and is launched by this init script:
#!/bin/sh -e
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: check_isp_connectivity
# Required-Start: $network
# Required-Stop: $network
# Default-Start: 3
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Check freebox connectivity
# Description: Check freebox connectivity
### END INIT INFO
NAME='check_isp_connectivity'
DAEMON='/usr/bin/check_isp_connectivity.sh'
PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin"
PIDFILE='/var/run/check_isp_connectivity.pid'
[ -x "${DAEMON}" ] || exit 0
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
case "$1" in
start)
echo "Starting check_isp_connectivity"
start-stop-daemon --start --background --quiet --exec $DAEMON
;;
stop)
echo "Stopping check_isp_connectivity"
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet --pidfile ${PIDFILE}
;;
status)
status_of_proc "$DAEMON" "$NAME" && exit 0 || exit $?
;;
*)
echo "Usage: /etc/init.d/check_isp_connectivity {start|stop}"
exit 1
;;
esac
It needs to get a daemon that will check the connectivity:
#!/bin/bash
# Check that the ISP2 works fine, and, if this is not the case, suppress balanced routing
# TODO : avoid multiple variable declaration between /etc/network/if-up.d/enable_balanced_routing and this script
# Interval to check connectivity on ISPs
check_interval=5
IFACE='eth2'
HOST='www.google.fr'
LOGFILE="/var/log/$(basename ${0/.sh/.log})"
PIDFILE="/var/run/$(basename ${0/.sh/.pid})"
INET1_IFACE='eth1'
INET1_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${INET1_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
INET1_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${INET1_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET1_GW='192.168.1.1'
INET1_WEIGHT=1
INET2_IFACE=${IFACE}
INET2_IFACE_IP=$(ip a s ${INET2_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {gsub("/.*", "", $2) ; print $2}')
INET2_NET_IP=$(ipcalc -n $(ip a s ${INET2_IFACE} | awk '($1=="inet") {print $2}') | awk '($1=="Network:") {print $2}')
INET2_GW='192.168.2.1'
INET2_WEIGHT=3
DO_RUN=true
# We catch SIGTERM signal to end this script properly
trap do_stop 15
function die()
{
echo "${@}" >&2
echo "$(LANG=C date "+%h %d %H:%M:%S") : ${@}" >> ${LOGFILE}
exit 1
}
function log()
{
echo "$(LANG=C date "+%h %d %H:%M:%S") : ${@}" >> ${LOGFILE}
}
function test_interface()
{
local test_ip=$(host -t A ${HOST} | awk '($2=="has" && $3=="address") {print $4}' | head -n 1)
# if balanced routing is disabled
if ! $(ip ro show | grep -Eq "nexthop via ${INET2_GW}"); then
ip route add to ${test_ip} via ${INET2_GW} dev ${INET2_IFACE}
if $(ping -W 1 -q -c 3 -I ${IFACE} ${test_ip} > /dev/null 2>&1); then
enable_balanced_routing
else
log "We cannot ping ${test_ip} and balanced routing is already disabled"
fi
ip route del to ${test_ip} via ${INET2_GW} dev ${INET2_IFACE}
# if balanced routing is enabled, and we cannot ping our test IP
elif ! $(ping -W 1 -q -c 3 -I ${IFACE} ${test_ip} > /dev/null 2>&1); then
log "We cannot ping ${test_ip}. Doing a second check just to be sure ..."
# We double check if we cannot join our test IP
if $(ping -W 1 -q -c 3 -I ${IFACE} ${test_ip} > /dev/null 2>&1); then
log "It's okay, I can ping ${test_ip} during the second test"
else
disable_balanced_routing
fi
fi
}
function disable_balanced_routing()
{
log "Disabling balanced routing"
ip route del default
ip route add default via ${INET1_GW}
ip route flush cached
}
function enable_balanced_routing()
{
log "Enabling balanced routing"
ip route del default
ip route add default scope global nexthop via ${INET1_GW} dev ${INET1_IFACE} weight ${INET1_WEIGHT} nexthop via ${INET2_GW} dev ${INET2_IFACE} weight ${INET2_WEIGHT}
ip route flush cached
}
function pid_managment()
{
local my_pid=$$
local old_pid
if [ -f ${PIDFILE} ]; then
old_pid=$(<${PIDFILE})
ps --no-headers --pid ${old_pid} >/dev/null && die "Deamon is already up and running"
fi
echo ${my_pid} > ${PIDFILE}
}
function do_stop()
{
log "${0} is stopping..."
DO_RUN=false
}
log "${0} is starting..."
pid_managment
# Launch check every x seconds
while ${DO_RUN}; do
if $(ip link show ${IFACE} | grep -q UP); then
test_interface
fi
sleep $check_interval
done
log "${0} is stopped"
Then we’ll set good rights and auto start on boot:
chmod 754 /usr/bin/check_isp_connectivity.sh /etc/init.d/check_isp_connectivity
update-rc.d defaults check_isp_connectivity
Resources
Last updated 20 Feb 2012, 18:13 +0200.